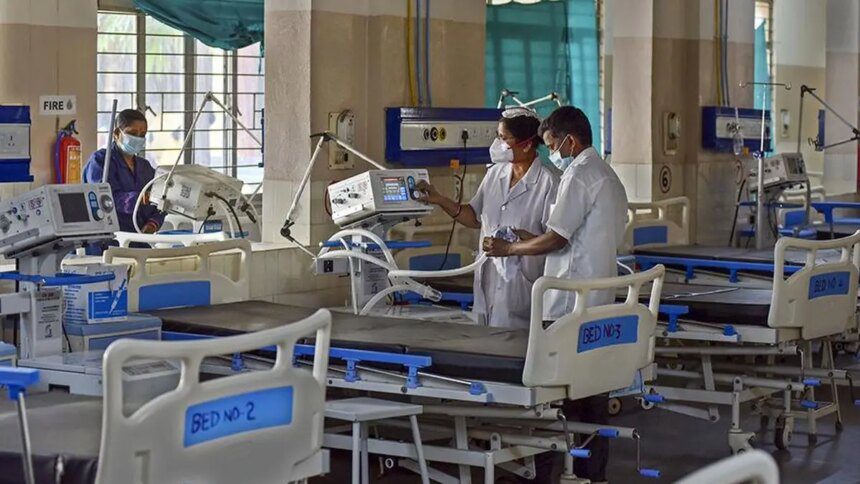
India’s healthcare sector is undergoing significant transformation, marked by the integration of advanced technologies and an emphasis on patient-centric care in an increasingly competitive landscape. Caregivers, essential to this evolving industry, often face work conditions that lack adequate training, safety protocols, and support systems. This issue presents not just a workforce challenge but a strategic risk requiring board-level attention, as neglecting it may diminish profitability, talent retention, and brand value.
The industry is currently experiencing a high attrition rate, driven by safety concerns alongside financial disparities. WebMD Health Services reports that the cost of replacing an employee can range from 30% to 200% of the annual salary of the departing employee. Additionally, when healthcare workers are injured or fall ill, the impacts extend beyond lost productivity, affecting care quality, financial health, and overall profitability. Consequently, healthcare organizations should prioritize the protection of their brand reputation and the retention of talented professionals, along with maintaining patient trust.
India’s legislation, including the Occupational Safety, Health and Working Conditions (OSH) Code, 2020, which specifically addresses healthcare workers, and various other regulations such as the Clinical Establishments Act, 2010, and the Indian Medical Council Act, 1956, highlight a regulatory framework for safety. Despite this, consistent enforcement and protection of healthcare professionals remain challenging.
Boards of healthcare organizations are urged to move from passive endorsement of policies to active governance, demanding regular updates on training progress, incident statistics, and feedback from frontline staff. Key performance indicators related to safety must be aligned with financial and patient satisfaction metrics to create a holistic view of organizational health. In a competitive market, establishing a brand through safety leadership can clearly set organizations apart. Additionally, public-private partnerships may enhance these efforts, helping fund mobile training units, shared safety infrastructures, and compliance technologies.
Creating a culture of safety begins at the top. Board-level commitment through investments in personal protective equipment (PPE), ongoing training, and established incident response systems can communicate strong support for healthcare workers. Moreover, the safety of healthcare workers should be recognized as a critical element of flourishing healthcare organizations. When boards treat safety as a strategic priority rather than merely a compliance issue, they can realize benefits such as reduced operational interruptions, enhanced patient outcomes, and improved financial performance.
When frontline staff feel secure, valued, and supported, their engagement increases, making them less likely to leave and improving the quality of care they provide. This leads to greater patient trust, which is crucial for both reputation and revenue. Leadership bears the responsibility of integrating workforce safety metrics into board discussions and fostering an environment that prioritizes safety. This dual focus on moral integrity and strategic advantage will be crucial for the future sustainability of healthcare delivery. The time has come for boards to decisively prioritize healthcare worker safety as essential to long-term organizational success.
(The writer is Managing Director, BD India/South Asia. Views are personal)
Published on December 1, 2025.